Difference between revisions of "Fluidized Bed Opposed Jet Mills"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
m |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Particle Size Reduction]]{{Knoppen}} | [[Category:Particle Size Reduction]]{{Knoppen}} | ||
[[File:Alpine_fluid_bed_opposed_jet_mill1.jpg|thumb|right|Fluid bed opposed jet mill principle]] | |||
[[File:Alpine_fluid_bed_opposed_jet_mill1.jpg|thumb|right|Fluid bed opposed jet mill]] | |||
[[File:Alpine_fluid_bed_opposed_jet_mill2.jpg|thumb|right|Fluid bed opposed jet mill]] | [[File:Alpine_fluid_bed_opposed_jet_mill2.jpg|thumb|right|Fluid bed opposed jet mill]] | ||
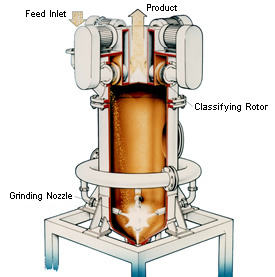
''' | '''Fluidized Bed Opposed Jet Mills''' rely purely on particle-to-particle attrition in the centre of a fluidized bed of material, this is achieved by focusing three or more compressed gas nozzles into the milling chamber which accelerates the particles to produce collisions where energy is released causing particle breakdown. | ||
Latest revision as of 23:37, 4 May 2014
Fluidized Bed Opposed Jet Mills rely purely on particle-to-particle attrition in the centre of a fluidized bed of material, this is achieved by focusing three or more compressed gas nozzles into the milling chamber which accelerates the particles to produce collisions where energy is released causing particle breakdown.
Features / benefits
- Consumes less energy than other conventional jet mills.
- Machine Range consists of 13 standard machine sizes with nominal air volumes of 50 to 1120 m³/hr, with four variants ensuring customised system modifications for specific applications.
- Operates with a minimum of wear.
- If required can produce "iron free" ultra fine powders.
- Noise emission less than 85 dB(A).
Applications
- Ultrafine size reduction of materials to Moh's hardness of 10.
- Powder finenesses of d97 = from 2 to 200 microns.
- Production of superfine powders without iron pick-up.
- Selective size reduction.
- Milling of temperature sensitive substances.
- Pharmaceutical powder processing as per GMP, FDA etc.